Definitions of thread terminology
Fundamental triangle
The fundamental triangle is the basic triangle that creates the thread form. For both parallel and taper thread, the tip angle of the fundamental triangle is symmetrical across a line that is perpendicular to the axis of thread. The fundamental triangle in parallel thread is an isosceles triangle (but not in taper thread).
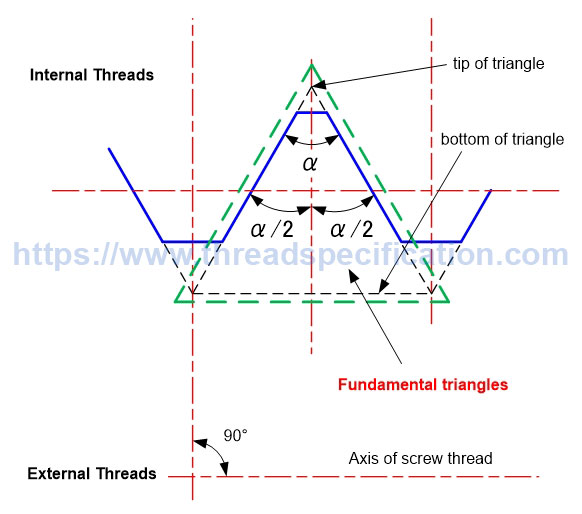
Parallel Thread
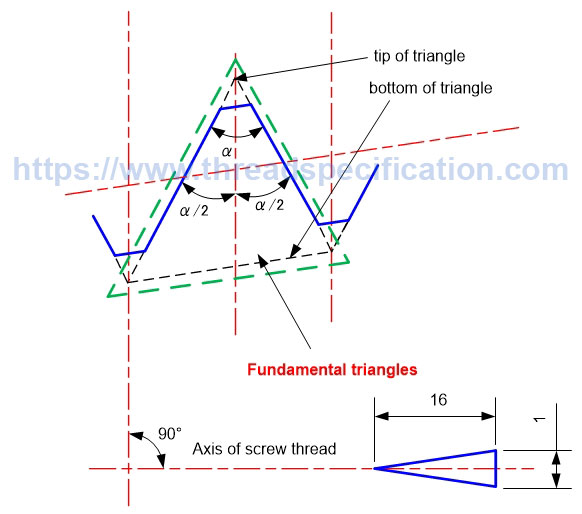
Taper Thread
Pitch
Pitch is the distance between two fundamental triangles of thread shape; it is measured along the axis of the thread. That is, if we turn the thread one round, it will travel a distance equal to one pitch.
For both parallel and taper threads, the definition of pitch is the same.
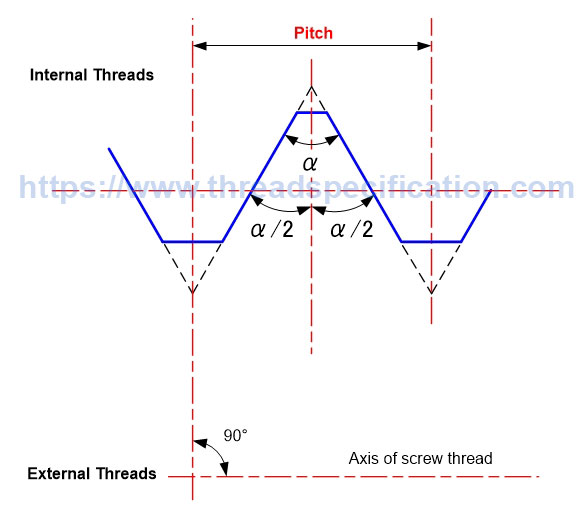
Parallel Thread
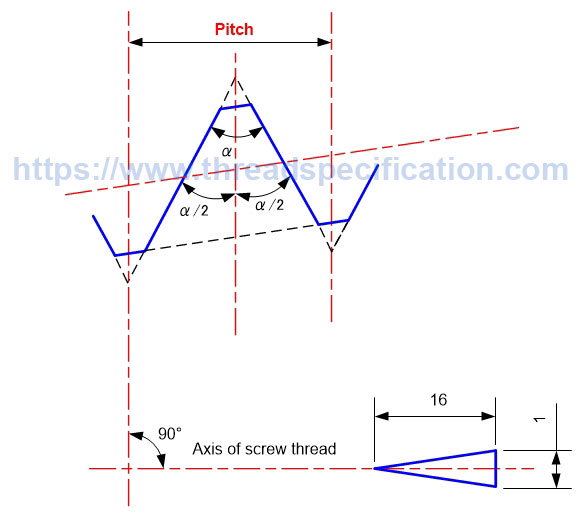
Taper Thread
Threads Per Inch TPI
TPI stands for Threads Per Inch, a count of the number of fundamental triangles per inch measured along the axis of the thread.
According to the definition of pitch, pitch is the distance between two fundamental triangles; thus, one pitch is equal to one inch divided by TPI. We have the following formula for the relationship between pitch and TPI: Pitch = 1/TPI (in) = 25.4/TPI (mm).
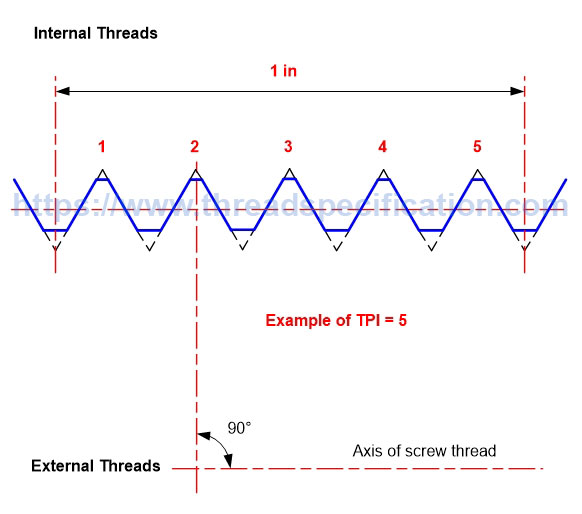
Parallel Thread
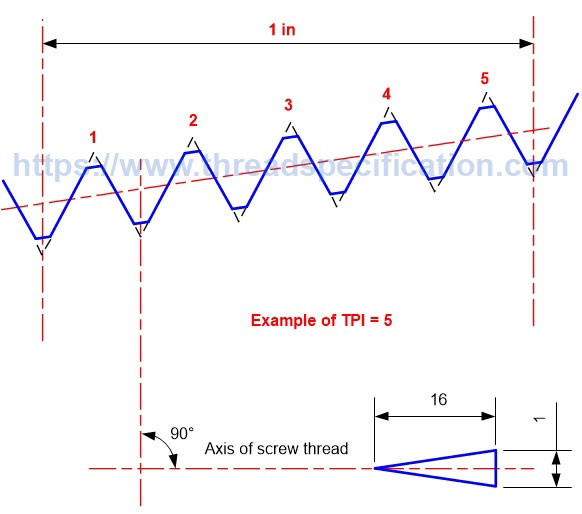
Taper Thread
Height of fundamental triangle
The height of a fundamental triangle is the distance from tip to bottom of the fundamental triangles; it is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of the thread. The height of the fundamental triangle determines the pitch diameter of the thread; the pitch diameter goes through the middle of the height of the fundamental triangle.
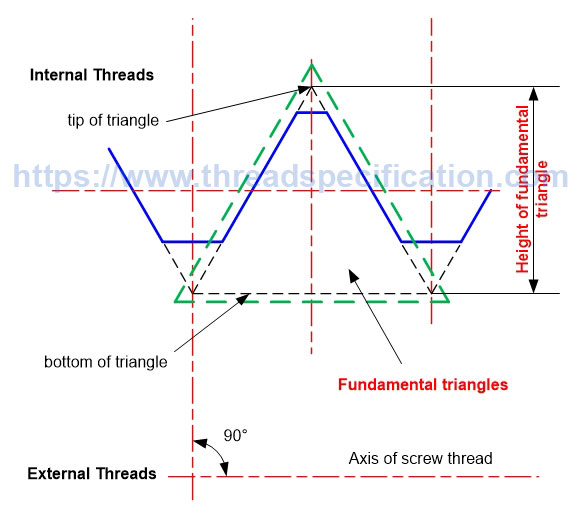
Parallel Thread
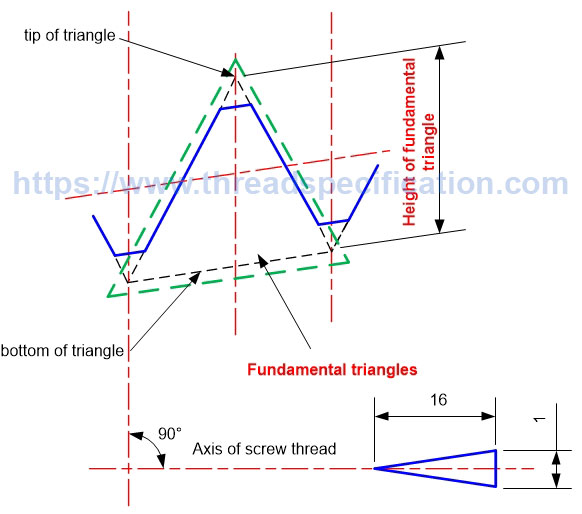
Taper Thread
Height of thread
The height of a thread is the distance from top to bottom of the thread; it is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of the thread.
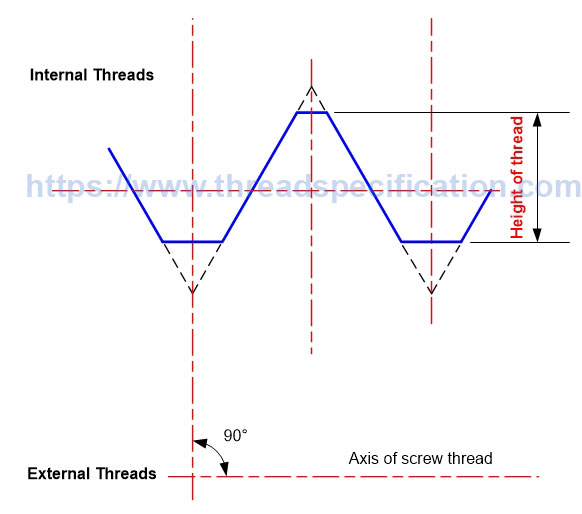
Parallel Thread
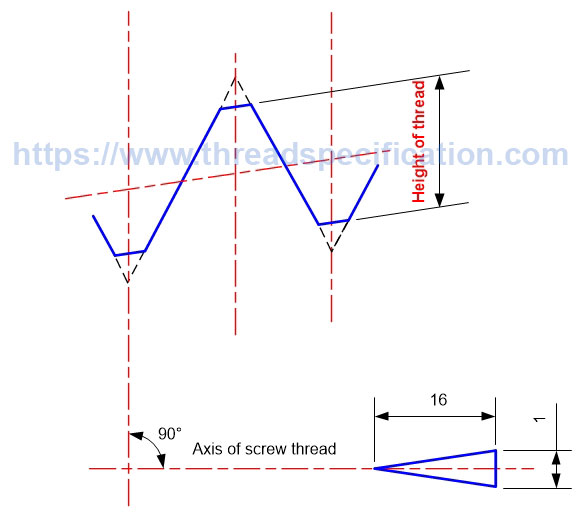
Taper Thread
Pitch diameter
The pitch diameter of thread is the diameter of a circle with the axis of thread as the center, and the radius is the distance from the middle of the height of the fundamental triangle to the axis of thread. It is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of thread. That means the pitch diameter goes through the middle of the height of the fundamental triangle.
In taper thread, the pitch diameter is measured at the gauge plane. See the profile of the thread for details on gauge.
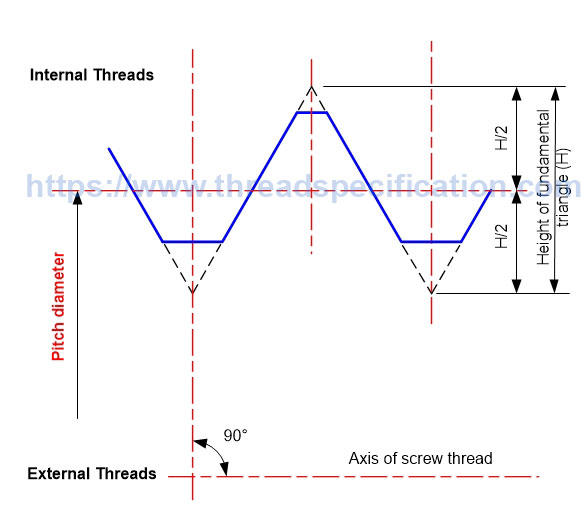
Parallel Thread
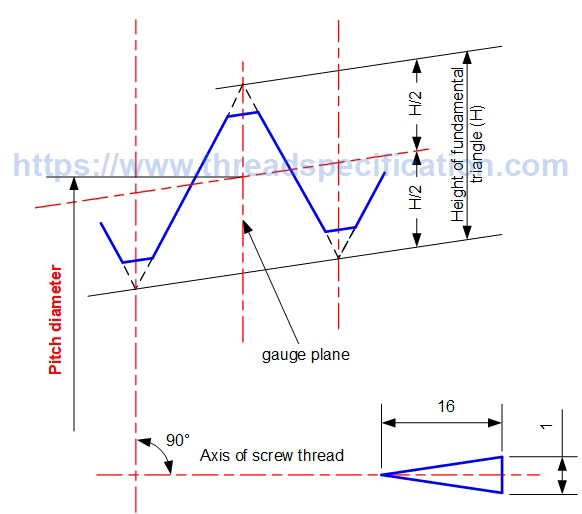
Taper Thread
Major diameter
The major diameter of internal thread is the diameter of a circle with the axis of thread as the center, and the radius is the distance from the bottom of the thread to the axis of thread. It is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of thread.
The major diameter of external thread is the diameter of a circle with the axis of thread as the center, and the radius is the distance from the top of the thread to the axis of thread. It is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of thread.
In taper thread, the major diameter is measured at the gauge plane. See the profile of the thread for details on gauge.
Major diameter of external thread:
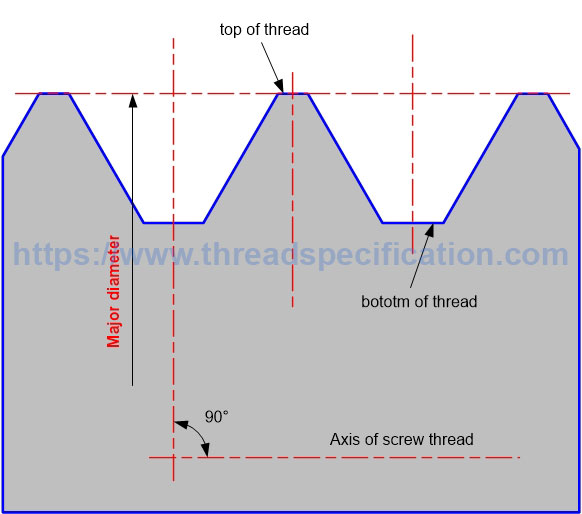
Parallel Thread
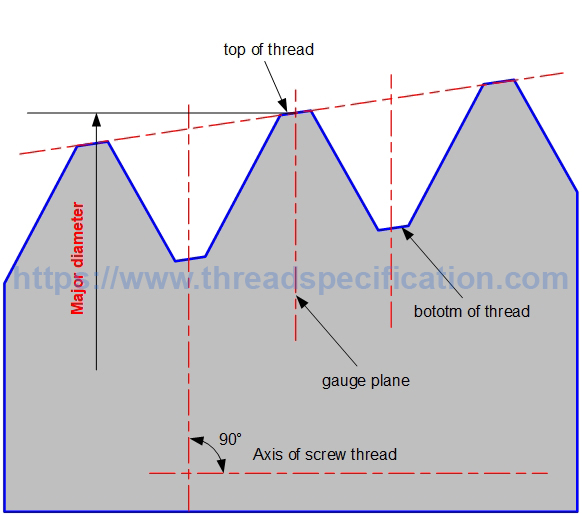
Taper Thread
Major diameter of internal thread:
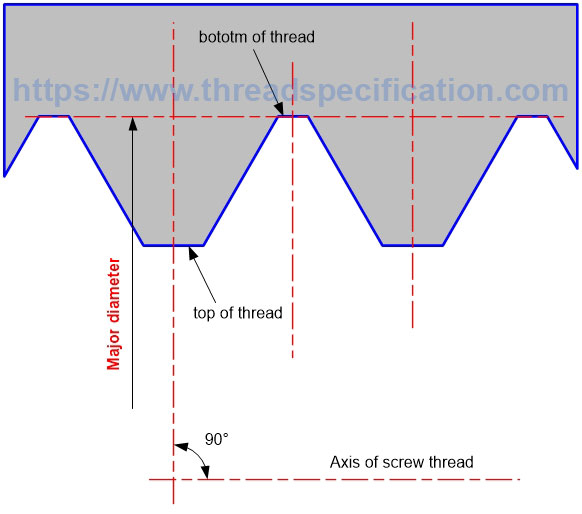
Parallel Thread
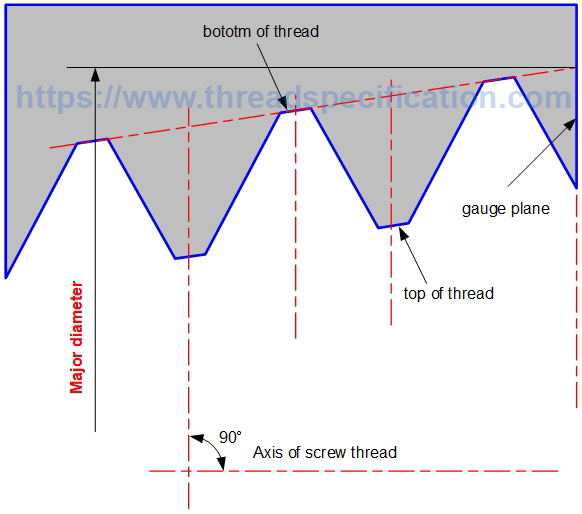
Taper Thread
Minor diameter
The minor diameter of internal thread is the diameter of a circle with the axis of thread as the center, and the radius is the distance from the top of the thread to the axis of thread. It is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of thread.
The minor diameter of external thread is the diameter of a circle with the axis of thread as the center, and the radius is the distance from the bottom of the thread to the axis of thread; it is measured in the direction perpendicular to the axis of thread.
In taper thread, the minor diameter is measured at the gauge plane. See the profile of the thread for details on gauge.
Minor diameter of external thread:
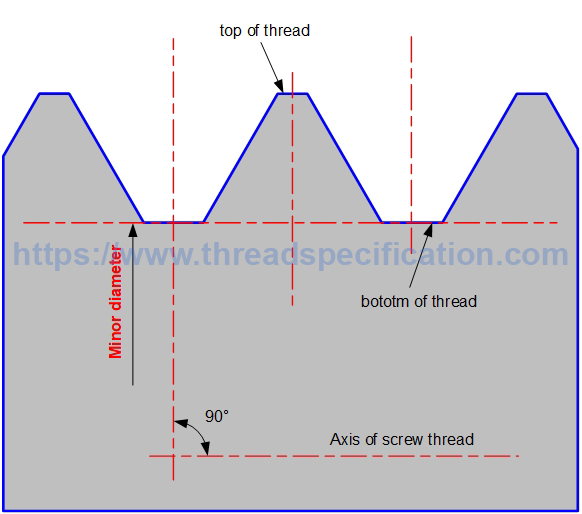
Parallel Thread
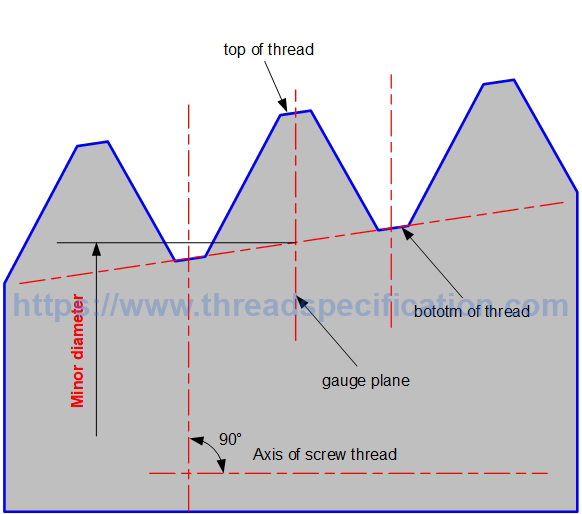
Taper Thread
Minor diameter of internal thread:
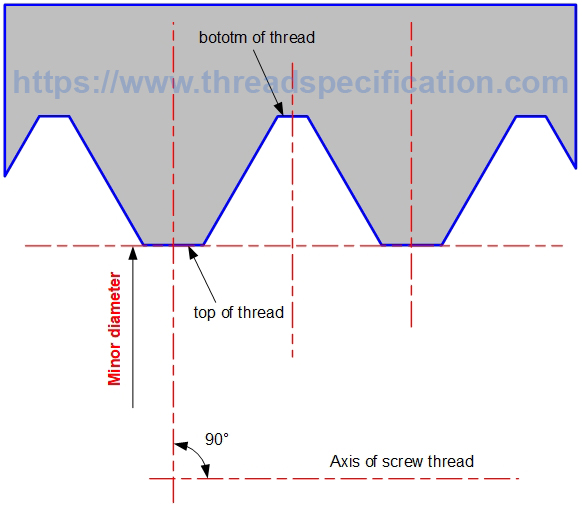
Parallel Thread
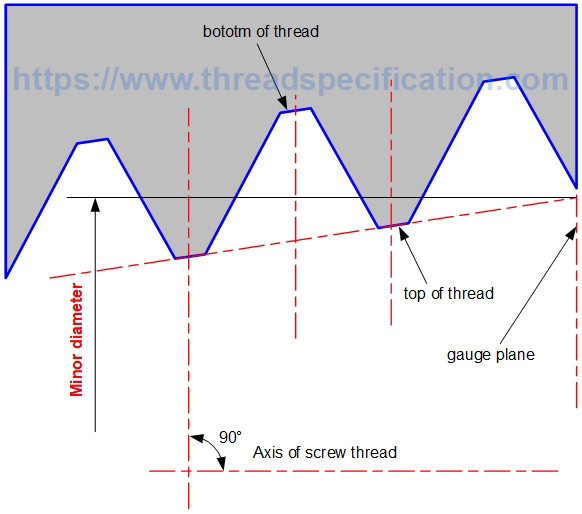
Taper Thread
Tolerance, Upper deviation, Lower deviation
The upper deviation is the upper limit of the diameter of the thread. The lower deviation is the lower limit of the diameter of the thread. The difference between an upper and lower deviation is defined as tolerance. Upper deviation – Lower deviation = Tolerance
The diameter of a thread in the following form:
Basic diameter
Upper deviation
Lower deviation
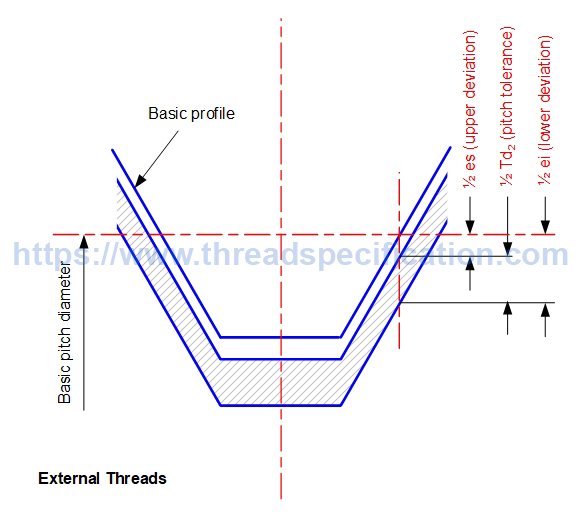
Tolerance on pitch diameter of external thread
Clearance on the crest
Clearance on the crest is the difference between the basic diameter and the design diameter of thread.
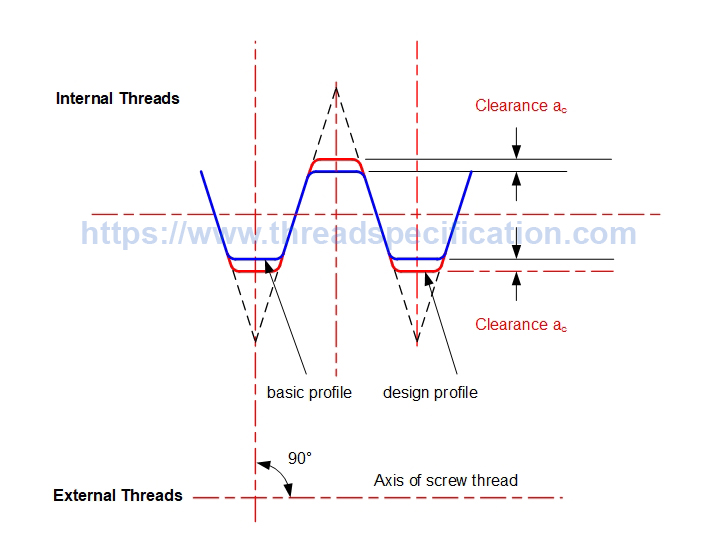
Clearance on the crest
Length of Thread Engagement
Length of thread engagement is measured by the length of interaction between the internal and external thread. In general, the length of engagement of mating threads is selected to utilize full tensile strength of a bolt prior to shearing of nut threads. Other applications may require internal thread shear prior to failure of the externally threaded part.
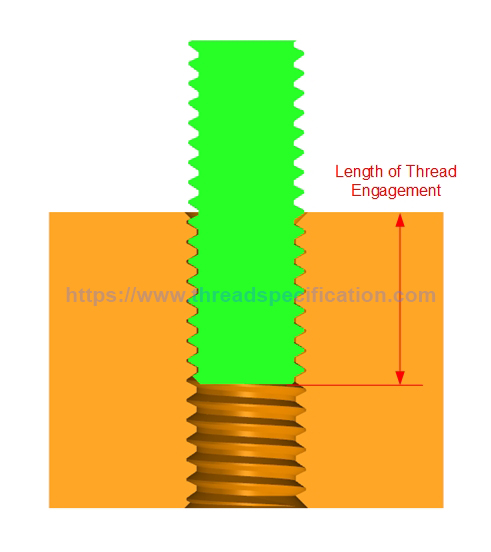
Length of Thread Engagement